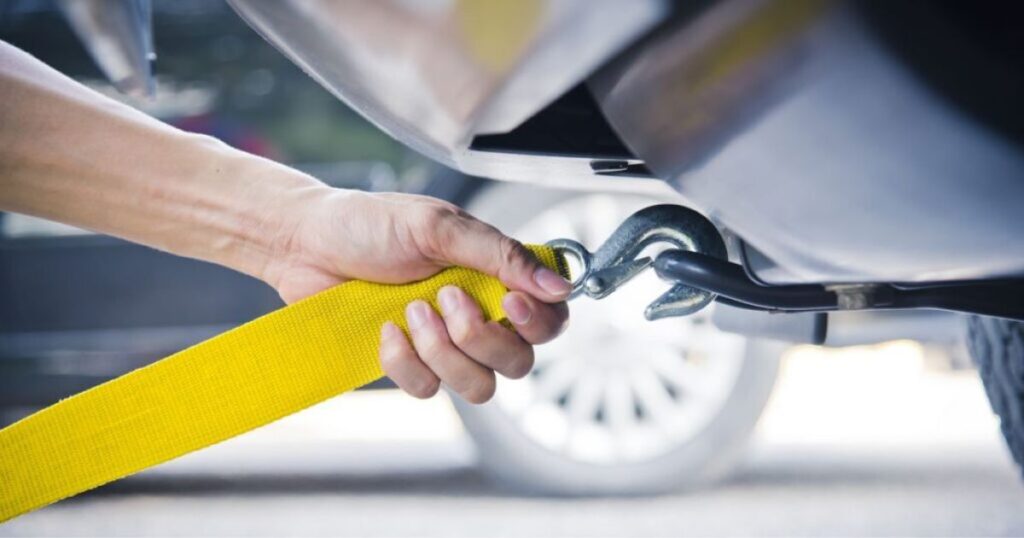
Car repossession is an unsettling prospect for any vehicle owner falling behind on auto loan payments. Unfortunately, it’s a reality that many borrowers face when financial hardships arise.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll understand the car repossession process, your rights and options, and how to navigate this challenging situation.
What Is Repossession?
Car repossession, or repo, occurs when a lender seizes a vehicle from the borrower due to delinquency or default on loan payments. Lenders have a legal right to reclaim the car if the borrower fails to fulfill their contractual obligation of making timely payments.
Repossession is typically a last resort measure taken by lenders after multiple missed payments and attempts to work out a resolution with the borrower.
How Car Repossession Works

The car repossession process usually follows a specific sequence of events:
- Missed Payments: If you miss one or more car loan payments, you are considered delinquent on your loan.
- Lender Notices: The lender will send you various notices, such as a “Notice of Default” or “Right to Cure Notice,” informing you that you have a certain period (typically 30 days) to bring the payments up to date or risk repossession.
- Repossession Agent Dispatched: If you fail to resolve the delinquency within the allotted time, the lender may hire a repo man or repossession agent to locate and seize your vehicle.
- Seizure of the Vehicle: The repossession agent will often attempt to locate and tow your vehicle without prior notice. They are legally allowed to take the car from public or private property if they do not breach the peace or cause property damage.
- Post-Repossession Options: After the repossessed car is taken, you may have options to regain possession, such as paying the outstanding balance, fees, and costs or negotiating a redemption or reinstatement plan with the lender.
It’s important to note that specific regulations bind repossession agents and cannot use force, threats, or illegal means to seize your vehicle. However, they can enter private property (like your driveway) to retrieve the car if they do not breach locked areas or gates.
What Lenders Can and Cannot Do When Repossessing a Car
Lenders have specific rights and limitations when it comes to repossessing a vehicle. Here’s what they can and cannot do:
What Lenders Can Do:
- Hire repossession agents to locate and seize the vehicle
- Enter private property (like your driveway) to retrieve the car, as long as they do not breach any locked areas or gates
- Charge you for repossession costs, storage fees, and any outstanding loan balance
- Sell the repossessed vehicle at auction or privately to recoup the remaining loan balance
What Lenders Cannot Do:
- Use physical force, threats, or illegal means to seize the vehicle
- Breach the peace or cause property damage during the repossession process
- Repossess the car before you default on the loan (missing payments alone does not constitute default)
- Fail to provide proper notices and disclosures about the repossession process
Repossession Laws and Regulations
Repossession practices are governed by various state and federal laws, including the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) and the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC). These laws outline lenders’ and borrowers’ rights and responsibilities during the repossession process.
Some key regulations include:
- Notice Requirements: Lenders must provide written notice to the borrower before repossessing the vehicle, typically in a “Notice of Default” or “Right to Cure Notice.”
- Breach of Peace Restrictions: Repossession agents cannot use force threats or cause property damage during repossession.
- Redemption Rights: In most states, borrowers have a certain period (often 10-60 days) after repossession to regain vehicle possession by paying the outstanding balance, fees, and costs.
- Surplus/Deficiency Laws: If the sale of the repossessed vehicle exceeds the outstanding loan balance, the lender must refund the surplus to the borrower. Conversely, the borrower may be liable for the remaining deficiency balance if the sale proceeds are insufficient to cover the loan balance.
Understanding your state’s specific laws and regulations regarding car repossession is crucial to protecting your rights.
Types of Repossession
There are different types of repossession scenarios that borrowers may encounter:
Voluntary Repossession
Sometimes, borrowers may voluntarily surrender their vehicle to the lender rather than waiting for an involuntary repossession. This can help avoid additional fees and potential legal complications.
Involuntary Repossession
This is the most common type of repossession, where the lender hires a repossession agent to locate and seize the vehicle without the borrower’s consent.
Self-Help Repossession
In certain states, lenders may be allowed to repossess the vehicle themselves without the involvement of a third-party repossession agent as long as they do not breach the peace or cause property damage.
It’s essential to understand your state’s laws regarding the different types of repossession and the specific procedures that must be followed.
How Repossession Affects Your Credit
Car repossession can have severe and long-lasting impacts on your credit score and financial standing. Here’s how it can affect your credit:
Late Payments
Even before repossession occurs, missing car loan payments will negatively impact your credit score. Late payments are reported to the major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion) and can significantly lower your credit score.
The Repossession of the Car Itself
The repossession event itself is a significant derogatory mark on your credit report and can severely damage your credit score. This negative item can remain on your credit report for up to seven years, making obtaining new credit or loans challenging.
Possible Court Judgment
If the sale of the repossessed vehicle does not cover the outstanding loan balance, the lender may pursue a deficiency judgment against you for the remaining amount owed. A court judgment can further negatively impact your credit score and may lead to wage garnishment or liens against your assets.
Rebuilding your credit after a repossession takes time and discipline, but it is possible with responsible financial habits, such as making timely payments on other debts and monitoring your credit reports for inaccuracies.
How to Avoid Repossession
Preventing repossession in the first place is the best course of action. Here are some tips to help avoid having your car repossessed:
Communicate with Your Lender:
Contact your lender immediately if you’re experiencing financial difficulties. Many lenders are willing to work with borrowers and may offer temporary payment relief or loan modifications.
Negotiate a Revised Payment Plan
Explore the possibility of renegotiating your loan terms, such as extending the loan period or temporarily reducing payments, to make them more manageable.
Seek Financial Assistance
Consider options like debt counseling services, credit counseling agencies, or government assistance programs that may help you get back on track with your car loan payments.
Voluntarily Surrender the Vehicle
If all else fails, consider surrendering the vehicle to the lender. While still damaging your credit, it can help avoid additional fees and legal complications associated with involuntary repossession.
Taking proactive steps and communicating openly with your lender can often lead to more favorable outcomes than ignoring the problem and risking repossession.
Recovering From Repossession
If your vehicle has already been repossessed, taking immediate action to mitigate the damage and begin the recovery process is essential. Here are some steps you can take:
Understand Your Redemption Rights
Most states give borrowers a period (often 10-60 days) after repossession to regain vehicle possession by paying the outstanding balance, fees, and costs. Familiarize yourself with your state’s redemption laws and act quickly if you wish to pursue this option.
Deal with Outstanding Debts
If you cannot redeem the vehicle or if there is a remaining deficiency balance after selling the repossessed car, work with the lender to negotiate a reasonable payment plan or settlement for the outstanding debt.
Dispute Inaccuracies on Credit Reports
Carefully review your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus and dispute any inaccurate or incomplete information related to the repossession.
How to Get a Repossessed Car Back
If you want to regain possession of your repossessed vehicle, you generally have a few options, depending on your specific situation and state laws:
Reinstatement
This option lets you bring your loan current by paying the missed payments, late fees, and associated repossession costs. Reinstatement puts your loan back in good standing, and you can continue making regular payments.
Redemption
In many states, you have a short window (typically 10-60 days) after the repossession to pay off the outstanding loan balance and repossession fees and costs to reclaim your vehicle. This can be expensive, but it may be worth considering if you can pay the total amount owed.
Attend the Auction
If the lender decides to sell your repossessed car at an auction, you can attend and bid on your vehicle. If you win the auction, you must pay the auction price plus any outstanding fees and costs.
- File for Bankruptcy: In some cases, filing for bankruptcy can temporarily halt the sale of your repossessed vehicle, giving you time to explore options for getting it back. However, bankruptcy should be a last resort and can have severe long-term consequences for your credit and financial well-being.
Act quickly and explore all available options to increase your chances of recovering your repossessed vehicle. Additionally, be prepared to negotiate with the lender and have a solid plan for staying current on payments if you regain possession of the car.
Repairing Your Credit After Repossession
A car repossession can significantly negatively impact your credit score, but it is possible to rebuild your credit over time. Here are some tips for repairing your credit after a repossession:
Check Your Credit Reports
Obtain copies of your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion) and review them carefully for any inaccuracies or errors related to the repossession. Dispute any incorrect information with the credit bureaus.
Make All Payments on Time
Payment history is the most significant factor affecting your credit score. Make all future payments (credit cards, loans, utilities, etc.) on time and in full to demonstrate responsible credit behavior.
Consider a Secured Credit Card
If your credit score is severely damaged, a secured credit card can help you rebuild credit by making timely payments on a low-limit account.
Become an Authorized User
Ask a family member or friend with good credit to add you as an authorized user on their credit card account. Their positive payment history can help improve your credit score.
Monitor Your Progress
Check your credit reports regularly to ensure that the negative impact of the repossession is gradually decreasing and that your credit score is improving over time.
Repairing your credit after a repossession takes patience and discipline, but it is essential to regaining financial stability and achieving your future goals.
Financial Assistance for Car Repossession

If you’re struggling to make your car loan payments and facing the risk of repossession, there are various financial assistance resources available that may be able to help:
Credit Counseling Agencies
Non-profit credit counseling organizations, such as the National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC), can provide guidance and negotiation assistance with your lenders and develop debt management plans to help you get back on track.
Legal Aid Services
Suppose you’re facing legal issues related to the repossession process. In that case, you may be eligible for free or low-cost legal assistance through organizations like Legal Aid or your state’s bar association.
Government Assistance Programs
Depending on your financial situation and location, you may qualify for government assistance programs that provide temporary relief or help with transportation costs.
Community Organizations
Local charities, religious organizations, or non-profits may offer emergency financial assistance or resources to help you keep your vehicle and avoid repossession.
Loan Modification Programs
Some lenders offer loan modification programs that can temporarily reduce your monthly payments or extend the loan term, making it more manageable during financial hardships.
It’s essential to explore all available options and seek assistance early on before the repossession process escalates. Being proactive and seeking help can increase your chances of finding a favorable solution.
Read More Posts
Comprehensive Guide To Vehicle Service History Checks
Best 0% APR Car Deals: May 2024
FAQs
What happens if the repo man never finds your car?
The lender may continue legal action to locate and repossess the vehicle.
What does it mean when a car is assigned for repossession?
It indicates the lender’s initiation of reclaiming the vehicle due to missed payments or default.
What do you say to avoid a repossession?
Communicate with the lender, explain your situation, and explore payment options.
How many days late can you be on a car payment before repo?
Typically, repossession can occur after just a few days of missed payments, depending on the lender and state laws.
Conclusion
Car repossession is a stressful and potentially damaging experience, but understanding the process and your rights can help you navigate this challenging situation more effectively.
Remember, open communication with your lender, exploring all available options, and taking proactive steps to address financial difficulties can often lead to better outcomes.
If you face repossession, don’t hesitate to seek assistance from credit counseling agencies, legal aid services, or other financial resources.
Rebuilding your credit and financial standing after a repossession is possible with patience, discipline, and responsible financial habits.
Ultimately, the best way to avoid the car repossession process altogether is to consider your ability to make consistent loan payments before taking on an auto loan.
Responsible borrowing and proactive communication with lenders can help prevent financial hardships from escalating to repossession.