Imagine the convenience of an electric vehicle (EV), but have you considered the potential risks of its lithium-ion battery pack? While lithium-ion batteries power our daily tech, they require careful handling in automotive applications to mitigate fire hazards. Let’s explore the safety factors surrounding these powerful energy sources in the cars we drive.
Lithium-ion batteries have become ubiquitous, found in everything from smartphones to power tools. Their high energy density, lightweight design, and rechargeable nature make them an attractive choice for EV manufacturers. However, these same qualities that make lithium-ion batteries so useful also introduce potential safety concerns, especially when scaled up to the larger battery packs required for electric cars.
Understanding Lithium-Ion Battery Basics
Before delving into the risks, it’s essential to understand how lithium-ion batteries work. These batteries rely on the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode to store and release energy. The electrolyte solution acts as a conduit for these ions, while the separators prevent short-circuiting between the electrodes.
The benefits of lithium-ion batteries are clear: they offer a high energy density, meaning more power can be packed into a smaller, lighter package compared to older battery technologies. They’re also rechargeable, making them a more sustainable and cost-effective option in the long run.
However, the drawbacks stem from the reactive nature of the lithium-ion chemistry. If the battery is damaged or defective, it can trigger a phenomenon known as thermal runaway, a rapid and uncontrolled temperature increase that can lead to fires or explosions.
Why Are Lithium-Ion Car Batteries Concerning?
While the risks associated with lithium-ion batteries are present in any device that uses them, the larger battery packs found in electric vehicles amplify these concerns. A single EV battery pack can contain thousands of individual lithium-ion cells, each with the potential for thermal runaway if not properly managed.
If thermal runaway does occur in an EV battery, the resulting fire can be extremely hot and difficult to extinguish. These fires are notoriously challenging to put out due to the high energy density of the batteries, as well as the potential for reignition even after the initial flames have been extinguished.
Several high-profile incidents have highlighted the dangers of lithium-ion battery fires in EVs. In 2023, a Tesla Model S caught fire while parked at a charging station in California, with the blaze eventually spreading to nearby vehicles. Similarly, a Hyundai Kona Electric was involved in a fire incident in Montreal, Canada, that same year, raising further concerns about the safety of these battery packs.
Read This Blog:How Much Does It Cost To Charge An Electric Car?
Main Causes of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires
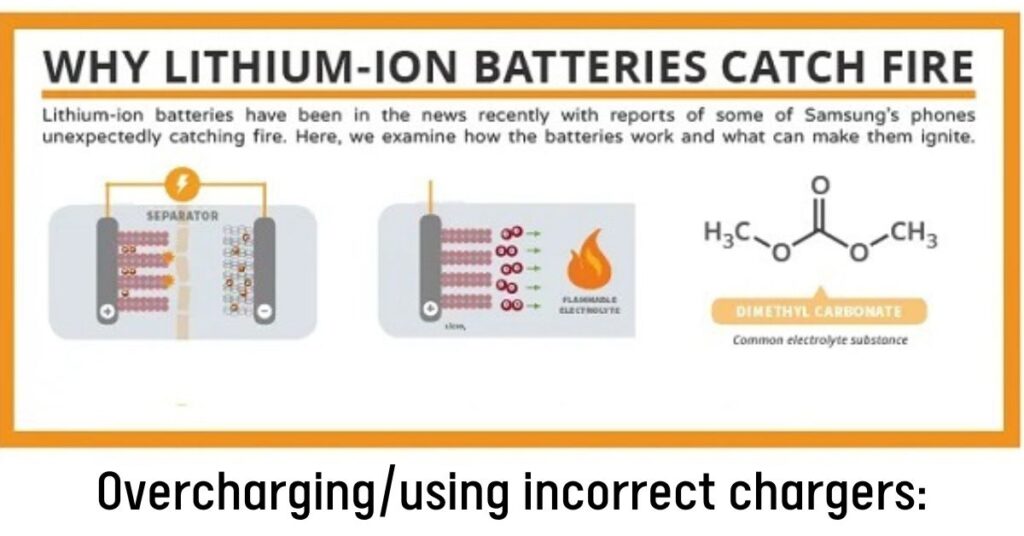
While the risk of thermal runaway is inherent to the lithium-ion chemistry, several factors can increase the likelihood of a fire occurring:
- Overcharging/using incorrect chargers: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to overcharging, which can lead to the deposition of lithium metal on the electrodes, creating a fire hazard. Using chargers not approved by the manufacturer or failing to follow proper charging protocols can contribute to this issue.
- Short-circuiting: If the separators between the anode and cathode are compromised, it can lead to an internal short circuit, rapidly discharging the battery and generating excessive heat.
- Overheating: Exposing lithium-ion batteries to high temperatures, either externally or through excessive internal heating during use, can trigger thermal runaway.
- Physical damage: Punctures, crushing, or other forms of mechanical damage to the battery cells can compromise their integrity and increase the risk of short-circuiting or thermal runaway.
- Manufacturing defects: Imperfections in the battery’s construction, such as faulty separators or contaminated electrolyte, can also lead to safety issues.
Manufacturer Precautions
Automakers are well aware of the risks associated with lithium-ion batteries and have implemented various safety measures to mitigate them. One common approach is to divide the battery pack into smaller, individual cells separated by firewalls. This design helps contain any thermal runaway event and prevents it from propagating throughout the entire pack.
Additionally, manufacturers are exploring the use of less flammable electrolyte solutions and alternative battery chemistries that may be less prone to thermal runaway. Some EVs also feature advanced battery cooling systems to help regulate temperatures and prevent overheating.
Despite these precautions, ongoing research and development into safer lithium-ion battery designs and materials will be crucial as the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow.
Safe Charging Best Practices

Proper charging practices are essential for maintaining the safety and longevity of lithium-ion batteries in EVs. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Use approved chargers: Only use chargers that have been approved by the vehicle manufacturer for use with your specific EV model. Third-party or counterfeit chargers may not follow proper safety protocols and could increase the risk of overcharging or electrical faults.
- Check for damage: Inspect both the charging cable and the vehicle’s charging port for any signs of damage before connecting. Frayed cables or bent connectors could lead to short circuits or overheating.
- Ventilate charging areas: Ensure that the area where you’re charging your EV is well-ventilated. Lithium-ion battery fires can produce toxic fumes, and proper ventilation can help mitigate this hazard.
- Avoid overnight charging: While it may be convenient, leaving your EV charging overnight or unattended for extended periods can increase the risk of fire if a malfunction occurs.
- Allow batteries to cool: Don’t immediately recharge your EV after a long drive or rapid acceleration, as the battery pack may be too hot. Allow it to cool down first to prevent overheating during charging.
By following these guidelines, you can help minimize the risks associated with charging lithium-ion batteries in your electric vehicle.
What to Do If a Lithium-Ion Battery Fire Occurs

Despite all precautions, there is always a chance that a lithium-ion battery fire could occur. If you notice any warning signs, such as swelling, leaking, or unusual odors coming from your EV’s battery pack, it’s crucial to act quickly and safely.
- Evacuate the area: If a lithium-ion battery fire has already started, evacuate the immediate area and move to a safe distance. These fires can produce toxic fumes and can quickly escalate.
- Call emergency services: Once you’re at a safe distance, call your local emergency services and inform them of the situation. Lithium-ion battery fires require specialized equipment and training to extinguish properly.
- Attempt to contain the fire (if safe): If the fire is still in its early stages and you have access to a lithium-ion battery fire extinguisher (more on these later), you may attempt to contain the fire. However, only do so if it’s safe and you’ve been trained in the proper use of these specialized extinguishers.
- Be prepared for reignition: Even if the initial fire appears to be extinguished, lithium-ion battery fires can reignite hours or even days later. Remain vigilant and be prepared to evacuate again if necessary.
It’s important to remember that attempting to extinguish a lithium-ion battery fire yourself can be extremely dangerous. If the fire has progressed beyond its initial stages, it’s best to evacuate the area and allow trained emergency responders to handle the situation.
Read More: Unlock Amazing Health Perks: Bike 10 Miles Daily
Proper Disposal and Handling
Proper disposal and handling of lithium-ion batteries is just as important as their safe use and charging. These batteries should never be discarded with regular household waste, as they can pose a fire risk during collection and processing.
Instead, follow these guidelines for safe disposal and handling:
- Use battery recycling points: Most municipalities and retailers offer designated battery recycling points where you can safely dispose of small, undamaged lithium-ion batteries.
- Handle damaged batteries with care: If a lithium-ion battery is swollen, leaking, or otherwise damaged, place it in a clear plastic bag and take it to a local hazardous waste collection facility or chemical cleanout event.
- Store batteries properly: When storing lithium-ion batteries, keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and combustible materials.
- Use approved transportation methods: If you need to transport used lithium-ion batteries, follow all applicable regulations and use approved packaging and labeling.
- Consider end-of-life options for EVs: As electric vehicles reach the end of their usable lifespan, automakers and regulatory bodies will need to establish safe and environmentally responsible methods for handling and recycling their large lithium-ion battery packs.
By following these guidelines, you
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that lithium-ion batteries are handled and disposed of safely, minimizing the risk of fires or environmental contamination.
Conclusion
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, addressing the safety concerns surrounding lithium-ion batteries will become increasingly important. While these batteries offer many advantages, their potential for thermal runaway and resulting fires cannot be ignored.
Manufacturers are taking steps to mitigate these risks, such as implementing advanced battery cooling systems, using less flammable materials, and dividing battery packs into smaller, isolated cells. However, proper charging practices, handling guidelines, and disposal methods are also crucial for maintaining safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are lithium batteries for cars safe?
Yes, lithium batteries for cars are generally safe when used and maintained properly. They offer benefits like longer lifespan and lighter weight compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Can I use a lithium-ion battery in my car?
Yes, you can use a lithium-ion battery in your car, but ensure it is compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system and meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
Can lithium-ion batteries be left in a car?
Lithium-ion batteries can be left in a car, but it’s best to avoid extreme temperatures as they can reduce battery life and potentially cause safety issues.
Is it safe to keep a power bank in a car?
It is generally safe to keep a power bank in a car, but avoid exposing it to very high or low temperatures, which can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan.
Is it bad to leave lithium batteries on the charger?
Yes, leaving lithium batteries on the charger for extended periods can lead to overcharging, which may reduce their lifespan and increase the risk of overheating or damage.